 View larger
View larger Relenza (Zanamivir) 5 Mg Rotadisc+Dischaler
RL9921
New product
| Quantity | Discount | You Save |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 5% | Up to $3.19 |
| 3 | 10% | Up to $9.57 |
| 4 | 15% | Up to $19.14 |
| 5 | 20% | Up to $31.90 |
Relenza 5 Mg Rotadisc+Dischaler ingredient Zanamivir
RELENZA Rotadisk
2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTUMATIC COMPONENT
Active ingredient: Each inhalation; Zanamivir (INN) 5 mg
Supplementary substances: Lactose monohydrate 25mg For other auxiliaries
Volume discounts
| Quantity | Discount | You Save |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | 5% | Up to $3.19 |
| 3 | 10% | Up to $9.57 |
| 4 | 15% | Up to $19.14 |
| 5 | 20% | Up to $31.90 |
More info
3. PHARMACEUTICAL FORM
Powder for inhalation
4. CLINICAL PROPERTIES
4.1. Therapeutic indications
Influenza therapy: Zanamivir is indicated for the treatment of both influenza A and B in adults and children (7 years old or older).
Prophylaxis: Zanamivir is indicated for the prophylaxis of both influenza A and B in adults and children (5 years old or older).
4.2. Posology and application form
Posology / application frequency and duration:
Influenza treatment:
• Adults;
The recommended zanamivir dose is two inhalations twice daily (2 x 5 mg) for five days, allowing a total daily dose of 20 mg to be administered.
To ensure maximum benefit, treatment should be started as soon as possible (within preferred two days) after the symptoms start to show.
01 / 17.09.09 / GDS12 1
Prophylaxis:
• Adults
Two inhalations (2x5mg) once daily for 10 days, providing a total of 10 mg dose daily for the recommended dose of zanamivir. If the exposures period of exposure is longer than ten days, the application period can be extended to one month.
Complete dose prophylaxis should be completed as prescribed.
Application method:
Zanamivir isthe Dischalerprovided
TM
administered to the respiratory tract only via oral inhalation usingdevice.
Zanamivir is also recommended to administer this drug before the onset of an onset drug, such as fast-acting bronchodilators.
Additional information on special populations:
Renal insufficiency: No dose modification is required (see Pharmacokinetic properties).
Hepatic failure: No dose modification is required (see pharmacokinetic properties).
Pediatric population: No dose modification is required (see pharmacokinetic properties). Geriatric population: No dose modification is required (see pharmacokinetic properties).
4.3. Contraindications Contraindicated in
those with hypersensitivity to any of the components of the preparation (see Qualitative and quantitative composition).
4.4. Specific use warnings and precautions
Influenza infection may be accompanied by an increase in respiratory hyperresponsiveness. Bronchospasm and / or decreased respiratory function have been reported in patients with influenza treatment and rarely in the history of some of them with respiratory illnesses, following very rare use of zanamivir. Such patients should stop taking zanamivir and undergo medical evaluation. Patients with respiratory disease should have a fast-acting bronchodilator available when taking zanamivir (see Posology and practice). Patients with rare hereditary galactose intolerance, Lapp lactose deficiency or glucose galactose malabsorption problem should not use this drug.
Influenza may be related to various neurological and behavioral symptoms. Three post-marketing reports (mostly from Japan and pediatric patients), influenza and zanamivir receiving
01 / 17.09.09 / GDS122
reported seizures, delirium, hallucinations and abnormal behaviors inpatients. These events are usually observed in the early stages of the disease and are often characterized by sudden onset and rapid cessation. Zanamivirin's contribution to these events has not been determined. If neuropsychiatric symptoms are present, the benefits and risks for each patient need to be assessed when treatment is continued.
It should not be used in children under 5 years old.
4.5. Interactions with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction
Zanamivir does not bind to proteins and is not metabolized or altered by the liver. Clinically significant drug interactions are unlikely.
Additional information on special populations No
data available.
Pediatric population: No
data available.
4.6. Pregnancy and lactation
General advice Pregnancy category is C
Women with childbearing potential / Contraception Studies on animals, pregnancy / and / or / embryonal / fetal development / and / or / birth / and / or postnatal development (see section 5.3). The potential risk to humans is unknown. RELENZA should not be used during pregnancy unless it is necessary.
Pregnancy period The safe use of Zanamivirin during pregnancy has not been established.
Reproductive studies on rats and rabbits have shown that zanamivir passes placenta. Studies on rats have shown no evidence of teratogenicity, fertility impairment or clinically significant perinatal or postnatal developmental failure following zanamivir administration. However, there is no information on human placental transfer. Zanamivir should not be used in pregnancy, especially if it is not more likely than the probable risk of fetus in the first trimester.
Lactation period It has been shown in rats that zanamivirin is injected with milk. However, there is no data on the mother's involvement. Zanamivir should not be used in suckling mothers if the experience is limited and the possible benefit to the patient is not more than the possible risk of fetus.
Reproduction ability / Fertility Not known.
01 / 17.09.09 / GDS12 3
4.7. Effects on vehicle and machine use
Unknown.
8.4. Adverse effects
Clinical trial data
Zanamivir is well tolerated when administered by oral inhalation. Adverse events reported in clinical trials, including studies on patients at high risk (in elderly patients and patients with chronic medical illnesses), are similar between the zanamivir and placebo groups.
Post-marketing data
The following events were identified when zanamivir was used for post-marketing influenza treatment.
The frequency classification is as follows: Very common ≥1 / 10 Common ≥1 / 100 and <1/10 Uncommon ≥1.000 and <1/100 Rare ≥1 / 10,000 and <1 / 1.000 Very Rare ≤ 1 / 10.000. Unknown (can not be estimated from the available data)
Immune system disorders Very rare: Percentage or allergic-type reactions including oropharyngeal edema.
Respiratory, thoracic disorders and mediastinal disorders Very rare: Bronchospasm, dyspnea.
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders Very rare: Rash, urticaria. Very rare: severe skin reactions including erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis
4.9. Overdose and treatment
Symptoms and Indications Zanamivir is not likely to be overdosed due to physical limitations of presentation, administration route and poor oral bioavailability (2-3%). No side effects were observed with oral inhalation doses of zanamivir up to 64 mg / day (approximately 3 times the recommended daily dose) (with nebulizer). In addition, systemic administration of iv up to 1200 mg / day for five days had no side effects.
Treatment is unknown.
01 / 17.09.09 / GDS12 4
5. PHARMACOLOGICAL PROPERTIES
5.1. Pharmacodynamic properties
Pharmacotherapeutic group: neuraminidase inhibitors ATC Code: J05A H01
Mechanism of Action
Zanamivir is a potent and highly selective inhibitor of the surface enzyme of influenza virus, neuraminidase. Viral neuraminidase aids in separating newly formed virus fragments from infected cells and can facilitate entry into the virus-mucinous epithelial cell surfaces, allowing viral infection to pass through other cells. The inhibition of this enzyme manifests itself in vitro and in vivo activity against influenza A and B virus replication and covers all known neuraminidase subtypes of influenza viruses.
Zanamivir shows its effect outside the cell. It inhibits the release of infectious influenza virions through the respiratory epithelial cells, thereby reducing both influenza and B viruses. Influenza viral replication is restricted by the superficial epithelium of the respiratory system. The efficacy of topical application of Zanamivirin to this region has been demonstrated in clinical trials. Clinical studies have shown that treatment of acute influenza infection with zanamivir causes a reduction in virus transmission from the respiratory tract without a detectable decrease in zanamivir susceptibility compared to placebo.
The pharmacodynamic effect is
unknown.
5.2. Pharmacokinetic properties General characteristics
Absorption: In oral pharmacokinetic studies the absolute oral bioavailability of the drug was low (mean 2%). In similar studies with orally administered zanamivir, systemic circulation of approximately 10-20% of the dose was found to reach the peak point within 1-2 hours of serum concentration. Poor absorption of the drug results in a low systemic concentration, so after oral inhalation zanamivir has not been systemically taken at an important location. After administration in the form of repeated oral inhalation, there is no evidence of a change in kinetics.
Distribution: Following oral inhalation, zanamivir is stored in intensive concentrations in the respiratory tract, so that the drug can be distributed to areas affected by influenza infection. Following a single dose of 10 mg, the concentration of zanamivir in the epithelium of airways, the place where the influenza virus replication was most intense, was measured. At the 12th and 24th hours, the concentration of zanamivirmean viral neuraminidase ICrespectively
50
was measured as 340 and 52 times the,. The high concentration of zanamivir in the respiratory systemviral neuraminidase inhibition
01 / 17.09.09 / GDS12 5
will result in a rapid onset of. The two main areas of accumulation were oropharynx and lungs (77.6% and 13.2% respectively).
Biotransformation: Zanamivir has been shown to be metabolised and unchanged from the kidneys and not metabolized.
Elimination: Zanamivir has a serum half-life of 2.6 to 5.05 hours after oral inhalation. If not completely changed urine is thrown. It is estimated that urinary clarensten total clearance is between 2.5 and 10.9 I / hr. Renal elimination is completed within 24 hours.
Characteristic characteristics of
patients Geriatric patients: Systemic exposure to zanamivir is not significant in patients with low bioavailability (10-20%) at daily 20 mg treatment doses. It is unlikely that there will be a change in pharmacokinetics that may have an age-related clinical significance and dose replacement is not recommended.
Pediatric patients: Zanamivirin pharmacokinetics was assessed on 24 pediatric patients from 3 months to 12 years of age using open label, one-dose study of nebulized (10 mg) and dry powder (10 mg). It has been determined that the prevalence of systemic exposure in children is equivalent to 10 mg of inhaled tobacco in adults.
Patients with renal impairment: The daily therapeutic dose of 20 mg is low (10-20%) of bioavailability and therefore systemic exposure to zanamivir is not significant. Given the breadth of Zanamivir's safety margin, a possible increase in exposure to patients with severe renal insufficiency is not a problem and dose adjustment is not necessary.
Patients with hepatic impairment: Zanamivir is not metabolized, so dosing is not necessary for patients with hepatic impairment.
Clinical Studies: Zanamivir alleviates and alleviates the symptoms when taken in healthy and high-risk patients as recommended for influenza treatment. When pool analyzes of phase III treatment trials (NAIB3001, NAIA3002, NAIB3002, and NAI30008) were performed, the mean duration of alleviation of influenza symptoms was 1.5 days (p less than 0.001) in patients receiving Zanamebi compared to placebo. Complications were 29% (208/711) in patients receiving placebo, compared with 22% (171/769) in patients receiving zanamivir (relative risk: 0.77; 95% CI: 0.65-0.92; p = 0.004). Antibiotic use for complication therapy was 19% (136/711) in patients receiving placebo, compared with 14% (110/769) in patients receiving zanamivir (relative risk 0.76; 95% CI: 0.60-0.95; p = 0.021).
Zanamivirin has been shown to be optimal at the onset of treatment as soon as possible after treatment has started.
01 / 17.09.09 / GDS12 6
It has been shown that zanamivir prescribed for prophylaxis prevents influenza in adults and children (5 years old or older). Zanamivir provides 67-79% protection compared to placebo when given at the recommended doses to protect against influenza and provides 56-61% protection compared to the group that is actively tested against the symptomatic influenza that has undergone laboratory confirmation.
5.3. Preclinical safety data
Zanamivir administration in toxicology studies on animals has not been associated with any clinical effect. Zanamivir is not genotoxic and there is no evidence of carcinogenic potential in long-term carcinogenicity studies on rats and mice.
6. PHARMACEUTICAL PROPERTIES
6.1. List of adjuvants
Lactose monohydrate
6.2. Incompatibilities Not
applicable.
6.3. Shelf life
7 years
6.4. Special precautions for storage
RELENZA30
°
should be stored at room temperature belowC.
6.5. The quality and content of the packaging
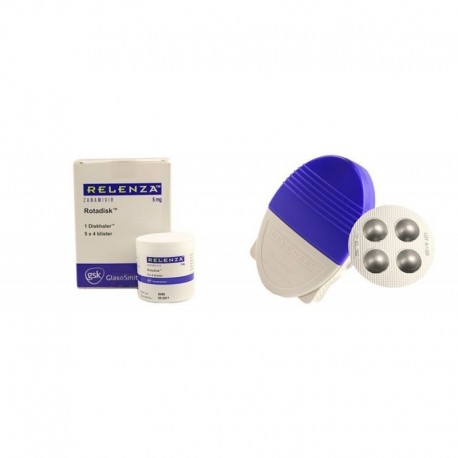
RELENZA consists of circular foil disctense (ROTADISK) with regularly dispersed 4 blisters each containing 5 mg zanamivir and 20 mg lactose. Dischaler is provided for administration of the drug.
6.6. Disposal of remaining materials and other special precautions for human medical products
Unused products or waste materials must be disposed of in accordance with the "Regulation on the Control of Medical Wastes" and the "Regulation on the Control of Wastes of Packaging and Packaging".
Instructions for use The
drug in powder form is drawn into the lungs with the breath. A disc containing medicament is placed in the disc hanger and the blister is opened when the tool is started.
For more detailed instructions for use, refer to the operating instructions for each patient in the package.
01 / 17.09.09 / GDS12 7
Instructions for use for patients Please read this instruction carefully before applying the first dose. If you are still not sure how to use the DISHWASHER, consult your pharmacist to have the instructions in hand with you.
Disc wheeler consists of three parts: Do not disassemble ROTADISK until you have stepped through the instruction.
01 / 17.09.09 / GDS12 8DIGITAL
ROTADISK is suitable to be placed inside the.
ROTADISK is suitable to be placed on the wheel. ROTADISK occurs in 4 blisters. Each blister contains a dose of RELENZA in powder form.
Important:
• Do not pierce any blades of ROTADIX before putting them in the RIDGE.
• You can keep a ROTADISK in doses between doses, but do not drill the blister until the desired intact.
• Keep OUTLET clean. After use, wipe the mouthpiece with a paper clip and close the blue mouthpiece cover between uses.
Mouthpiece Cover
Mouthpiece
Wheel
Finger
needle Needle
cover
clamps PunchSteps for using the RELENZA RACK
1. Remove the lid cover,
01 / 17.09.09 / GDS12 9
Make sure that the inner and outer parts are clean.
2. Hold onto the corners of the white table and gently pull out all the plastic tabs on the sides of the table until they are visible.
3. Place your thumb and index finger on these protrusions, press inward and pull the tab out from the main body.
The white body will be pulled out easily.
4. Place a new RELENZA ROTADISK on a dark colored wheel.
Make sure that the written part of the blister is placed at the top and the face at the bottom. The blisters are fully inserted into the gaps in the wheel.
5. Push the tab into the main body completely.
If you are not ready to immediately release RELENZA, install the blue nozzle cover.
For inhalation: Do not perform this operation until just before the dozens are inhaled.
6. Keep theKeep the
ROCKER horizontallyROCKER horizontally.
Lift up the cover as much as it can be lifted. The lid should be in the fully vertical position, making sure that the blister is completely pierced.
Push the cover back (close) Your headset is now ready for use. Keep your horizontal position as long as you do not want to die.
TROUBLESHOOTING: 7. DO NOT PRESS THE HEADQUARTER IF NOT IN YOUR HEART. Give your breath as easily as you can, lift the bow until your mouth is aligned. Do not blow into the bow.
01 / 17.09.09 / GDS12 10DINSER
Hold thehorizontally.
We are among your teeth. Close your lips tightly to surround the mouth. Do not bite your mouth, cover your lips tightly around your mouth. Do not close the air vents next to your mouth. Breathe continuously and deeply from your mouth. Keep your breath for a while. Remove the DISHWASHER from your mouth. Keep your breath comfortably as long as you can.
Prepare the next blister (the second part of your dose):
8. Pull as far as the white plate will be pulled out. (do not remove it completely), then push it back again.
01 / 17.09.09 / GDS12 11
Turn the wheel until the next blister appears. When you need to re-inhalate, bring the full blister to the position underneath the piercing needle. Repeat steps 6 and 7 again as you do.
9. After all the blows have been made (normally two blisters):
Clean the bristle paper wipe and replace the blue nozzle cover. It is important that you keep DIKKORA clean.
Renewing ROTADIX: When
all four blisters are empty, remove the ROTADIX from the rack and insert a new one, proceed as described in steps 1-5.

